WIF(Wallet Import Format)
Introduction to how private keys are encoded and recorded.
WIF Format
WIF (Wallet Import Format) is a method to represent Bitcoin private keys in a human-readable format, making it easier for users to import and export private keys between wallets. The WIF format encodes and verifies private keys to ensure their validity and security.
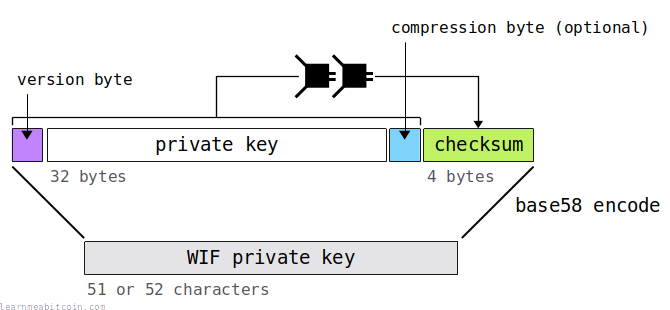
Encoding
The process of WIF encoding for a Bitcoin private key is as follows:
-
Generate Private Key: Use a random number to generate a 256-bit private key.
-
Add Version Prefix:
- For mainnet private keys, the prefix is
0x80. - For testnet private keys, the prefix is
0xEF.
- For mainnet private keys, the prefix is
-
Add Compression Flag (Optional):
- If using a compressed public key, add a byte
0x01after the private key. - This results in a shorter public key and reduces the transaction size.
- If using a compressed public key, add a byte
-
Calculate Checksum:
- Perform double SHA-256 hashing on the combined prefix and private key.
- Take the first 4 bytes of the hash result as the checksum.
-
Combine Data:
- Combine the prefix, private key, and checksum into a complete byte array.
-
Base58Check Encoding:
- Perform Base58 encoding on the combined byte array to generate the final WIF private key.
Encoding Example
Suppose we have a mainnet private key 0x1E99423A4EDF1000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000. The steps
for WIF encoding are as follows:
- Private Key:
1E99423A4EDF1000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 - Add Version Prefix:
801E99423A4EDF1000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 - Calculate Double SHA-256 Checksum:
- First SHA-256:
C32D3FE4CFAEAB72ABF8735B5283D014B726B448D1747FDC524E8F8633E1DD56 - Second SHA-256:
1C99E9B3F3E51E2F22E283B59C9AAB340084AE0D8FDC1FA83F3E9BEBFE4A01C2
- First SHA-256:
- Take First 4 Bytes of Checksum:
1C99E9B3 - Combine Data:
801E99423A4EDF10000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001C99E9B3 - Base58Check Encoding:
5J1F3H9ZC8QK6FPU9U5JJMWMAAFN7F5Q0Q1BPE0Z3MN4UHV1Q9F
The final WIF private key is 5J1F3H9ZC8QK6FPU9U5JJMWMAAFN7F5Q0Q1BPE0Z3MN4UHV1Q9F.
WIF Format Verification
The process of verifying a WIF private key is as follows:
- Base58 Decoding: Perform Base58 decoding on the WIF private key to obtain the byte array.
- Extract Data: Extract the prefix, private key, and checksum from the byte array.
- Checksum Verification:
- Perform double SHA-256 hashing on the extracted prefix and private key.
- Compare the calculated checksum with the extracted checksum.
- Prefix Verification: Ensure the prefix is a valid mainnet (
0x80) or testnet (0xEF) prefix.
If both the checksum and prefix are verified, the WIF private key is valid.
Distinguishing Mainnet and Testnet Private Keys
The WIF format distinguishes mainnet and testnet private keys primarily through the prefix:
- Mainnet Private Key: Prefix is
0x80, Base58Check encoded key usually starts with5. - Testnet Private Key: Prefix is
0xEF, Base58Check encoded key usually starts with9orc.
This prefix distinction ensures that mainnet and testnet private keys are not confused, avoiding the risk of misusing testnet coins on the mainnet or vice versa.
Summary
The WIF format provides a secure and user-friendly way to represent Bitcoin private keys for import and export between wallets. Through version prefixes, checksum mechanisms, and Base58Check encoding, the WIF format ensures the validity and human readability of private keys. Additionally, the prefix distinction between mainnet and testnet private keys further enhances the security and stability of the Bitcoin network. Understanding the encoding and verification process of the WIF format helps better manage and use Bitcoin private keys.